Do you find yourself grabbing your headphones several times a day? While it's an excellent way to stay connected and enjoy your favorite music, you may have experienced discomfort like itching or wetness in your ears. It's essential to ask, can headphones cause ear infections?
Your concerns are valid, especially when you consider the significant investment you've made in your audio gear. You don't need to abandon your headphones just yet.

This article delves into how headphones can potentially lead to ear infections and offers tips to maintain optimal ear health while enjoying your audio experience.
How Can Headphones Lead to Ear Infections
Indeed, inappropriate use of headphones can potentially lead to ear infections. But there's no need to ditch your beloved audio gear just yet. For instance, a study involving customer service reps who consistently wore headphones found a less than 3% incidence rate of chronic middle ear infection, with no external ear canal infections recorded.
However, another study indicated that excessive use of headphones can foster bacterial growth, leading to infection. This situation arises because earbuds can obstruct airflow, leading to moisture build-up and promoting bacterial growth.
It is essential to remember that the presence of bacteria does not always result in an infection. But a significant, unchecked increase in bacterial growth can certainly contribute to the problem.
Thus, the headphones you use, how you clean and sterilize them, and how long you wear them all have an impact on your ear health.

What Triggers Ear Infections
Let's delve into what actually happens when we use headphones or earbuds.
Bacteria and Moisture
Your ear canals offer a dark, moist environment, conditions that bacteria find quite favorable. When we use earbuds, we can inadvertently disrupt the balance of this environment, leading to an increase in bacterial growth. Prolonged usage can also block the ear canal, resulting in trapped moisture which further invites bacteria.
Earwax Impaction
Earwax keeps our ears clean by keeping bacteria, viruses, dust, and other things from getting into them. But problems happen when earwax gets pushed back into the ear. This is called "earwax impaction," and it's often caused by using earbuds over and over again. This stuck wax creates a blockage, which lowers the protective layer in your ear, keeps moisture and old wax from getting in, and sets the stage for an illness.
Ear Canal Scrapes
Frequent, rough insertion of earbuds can cause scrapes in the ear canal, breaking through the protective layer of earwax and causing potential infection. It's advisable to gently insert earbuds, and consider custom or semi-custom fit earbuds to avoid injury.
Signs of an Ear Infection
Dr. Ralph says, "Indications of an ear infection include ear pain, itching, discharge from the affected ear, or hearing impairment."
Additional symptoms may encompass a clogged sensation, inner ear stabbing pain, nausea, or even fever. Any temperature above 100.4 degrees is considered a fever by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Treatment for external ear infections typically involves topical antibiotic drops, antifungal drops, or a topical steroid drop, depending on the identified cause, as per Dr. Ralph.

Ways to Prevent Ear Infections While Using Headphones
To avoid ear infections and keep your ears healthy, it's crucial to follow some simple, effective strategies.
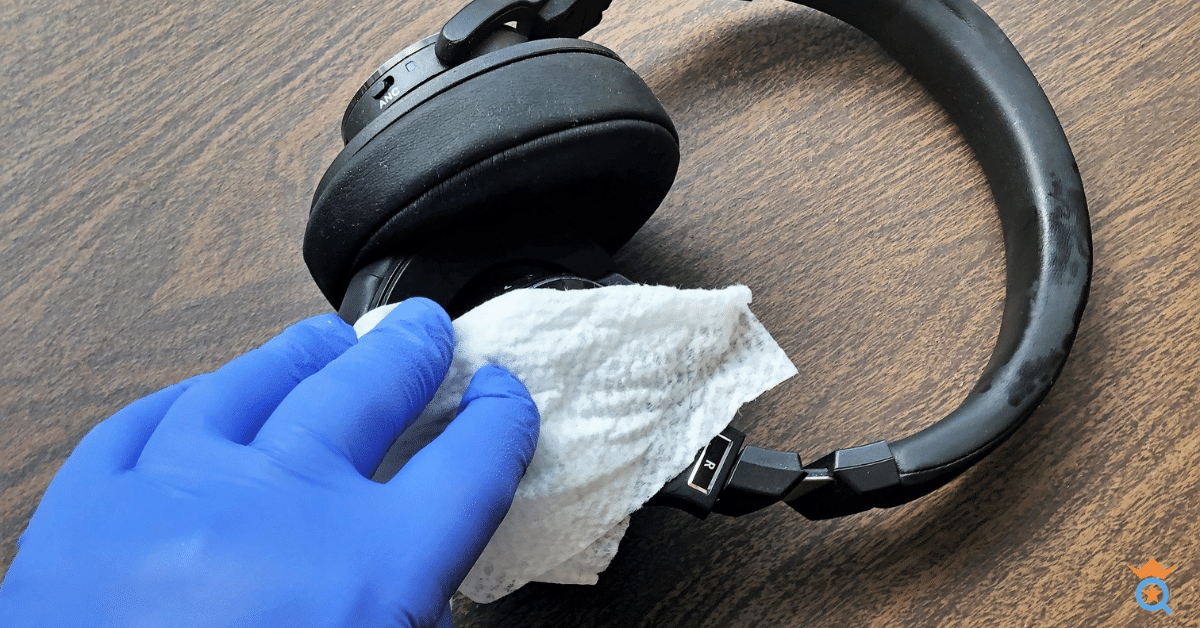
1. Maintain Cleanliness of Headphones and Ears
Regular cleaning and sanitizing of your headphones or earbuds can significantly help prevent infections. Cleaning should ideally be done weekly or anytime you notice visible dirt or earwax on your earbuds.
Keeping your ears clean is also important. Washing the outside of the ear with a wet cloth can help. If you're dealing with earwax buildup, consider using an earwax softener or consulting a healthcare provider for safe methods of ear cleaning.
2. Don't Share Your Headphones
While it might seem romantic or friendly to share an earbud with someone else, this practice can spread bacteria and potentially lead to ear infections. If you absolutely must share headphones, consider using disposable headphone covers or thoroughly cleaning the headphones before use.
3. Give Your Ears Time to Breathe
Overuse of headphones can indeed cause ear infections by limiting airflow to the ears and trapping moisture and earwax. Prolonged usage also risks noise-induced hearing loss due to high volumes.
Therefore, try limiting your headphone usage to 90 minutes at a time at 80% volume, as recommended by audiologists.
If you wish to extend this period, consider reducing the volume further and taking regular breaks.

Other Health Issues Associated with Headphone Use
The focus has been on headphones and ear infections but improperly utilizing headphones and earbuds can create additional health issues. Let's discuss some of the common problems associated with headphone usage, highlighting the significance of maintaining good ear health.
1. Hearing Loss & Impairment
Loud music, especially through headphones, can damage hearing. High-volume sounds can permanently damage the inner ear, causing hearing loss. It can also produce hyperacusis and tinnitus, a persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. Reduce headphone volume and duration to avoid hearing loss.
2. Ear Pain
While ear pain is frequently connected with ear infections, it can also result from incorrectly wearing headphones or earbuds. Ill-fitting or overly tight headphones can exert pressure on the outer ear or strain the sensitive inner-ear cartilage, leading to discomfort.
To alleviate ear pain, opt for headphones with padding materials such as memory foam, velour, or leather. Consider custom-made or semi-custom-fit earbuds or in-ear monitors (IEMs) to ensure a perfect fit for your ears.
3. Ear Numbness and Acoustic Shock Injury (ASI)
Ear numbness can occur due to similar reasons to ear pain. Wearing headphones that are too tight or not properly sized can contribute to numbness. Additionally, frequent users of headphones, such as individuals working from home, may experience a condition called Acoustic Shock Injury (ASI).
ASI is triggered by sudden exposure to uncomfortably loud sounds, often caused by grounded noises from headphones or loud echoes. Burning, numbness, a sense of obstruction, tinnitus, vertigo, and psychological shock are among the symptoms.
Using looser headphones, appropriately sized earbuds/IEMs, and practicing proper usage can help prevent these issues.
4. Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear)
Otitis Externa, commonly known as swimmer's ear, can also be caused by headphone usage. It typically starts as an itchy rash and can become painful if left untreated.
While water exposure is a common cause, we focus on the route of injury. Roughly inserting earbuds or other objects into the ears can result in scrapes on the ear canal, making the ear vulnerable to infection.
Additionally, headphones that break through the protective layer of earwax can also increase the risk of Otitis Externa. Proper hygiene practices, including gentle insertion of earbuds, regular cleaning, and avoiding sharing headphones, can help prevent this condition.
Final Verdict
While ear infections have been the primary concern regarding headphone usage, it's crucial to recognize the broader spectrum of health issues associated with improper use.
By being aware of these risks and following recommended guidelines, such as limiting volume, maintaining proper fit, and practicing good hygiene, you can mitigate the chances of experiencing hearing loss, ear pain, numbness, and conditions like Otitis Externa.
Prioritizing your ear health and taking proactive measures will ensure a safe and enjoyable listening experience.
Frequently Ask Questions
Is it bad to wear in-ear headphones all day?
Wearing in-ear headphones all day can pose potential risks to your ear health. In-ear headphones can cause earwax and moisture buildup, promoting bacterial growth. To avoid ear infections, take pauses from wearing headphones, let your ears breathe, and practice good hygiene.
What are the symptoms of ear damage due to headphones?
Symptoms of ear damage due to headphones can vary, but some common signs include: Persistent ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears (tinnitus), Difficulty hearing or understanding conversations (hearing loss), Sensitivity to certain sounds (hyperacusis)
Ear pain or discomfort, Itching, redness, or irritation in the ear canal, Discharge or fluid from the ear.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
How do you prevent ear infections from headphones?
To prevent ear infections caused by headphones, consider the following measures:
Keep your headphones clean and sanitized regularly, especially the ear tips or cushions that come in direct contact with your ears.
Avoid sharing headphones or earbuds with others to minimize the risk of bacterial transmission. Take breaks from wearing headphones to allow your ears to breathe and prevent moisture accumulation.
Can headphones cause ear irritation?
Yes, headphones can irritate your ears, especially if they do not fit properly or if you are allergic to the materials used in the headphones. Poorly fitting headphones or earbuds can irritate, redden, or strain the inner-ear cartilage or outer-ear flesh. Hypoallergenic headphones with ear-friendly cushioning reduce inflammation.
How do you treat an ear infection from earbuds?
If you suspect an ear infection from using earbuds, it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. Treatment options for ear infections may include Prescription of antibiotic eardrops or oral antibiotics to eliminate the infection. Cleaning the ear canal to remove any impacted wax or debris. Avoiding the use of earbuds or headphones until the infection has healed.








